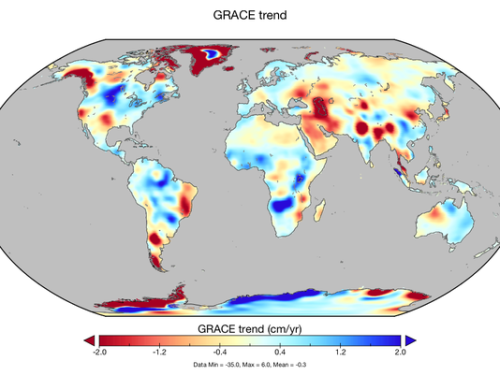
Image: NASA, based on study by Matthew Rodell, et al, 2018
U.S. space agency NASA’s new analysis of 14 years of satellite data shows rapid change in the world’s freshwater supply in startling detail never captured before. The 34 “trends” in the data picture not only the effects of climate change, like worsening droughts, but of human over-use, such as pumping out underground aquifers to irrigate crops. To a lesser extent, they show natural change over time. They also indicate where water scarcity is most likely to reach crisis mode and lead to armed conflict over resources and/or forced human migration.
“There are implications in that map for food security, for water security and for human security in terms of things like conflict and climate refugees,” said Dr. Jay Famiglietti, a water-resources expert affiliated with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory and co-author of a paper on the findings in the journal Nature. He and other experts said the mapping should serve as a wake-up call for policymakers.
Read more:
NASA Satellites Reveal Major Shifts in Global Freshwater — NASA
Emerging Trends in Global Freshwater Availability — Nature
‘This Is an Eye-Opener’: Changes in Global Water Supply Hint at Future Conflicts and Crises — The Globe and Mail
Water Shortages to Be Key Environmental Challenge of the Century, NASA Warns — The Guardian
NASA Finds ‘Human Fingerprint’ in Many Areas of Water-Supply Change Worldwide — USA Today
First Map of Global Freshwater Trends Show Human Fingerprint — Axios
Related posts:
California Drought: Overcoming History to Reduce SoCal Water Waste
Study Finds We Vastly Underestimate Water Management’ s Depletion of Groundwater
It’s Long Past Time to Police Big Agriculture’s Water Waste
World Water Day: UN World Water Development Report Warns of Global Crisis by 2030
At the Point of ‘Peak Water,’ Our Foreseeable Future Grows Shorter
Mapping the World’s Most Water-Stressed Countries
Serious Water Conservation Demands Layered Approach and Emotional Commitment
Study: Freshwater Shortage Will Double Climate Change’s Impact on Agriculture
Unchecked Emissions Will Drain Water Resources, Warns Leaked U.N. Report











